What Is Folliculitis? Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, Products Recommended
What Is Folliculitis?
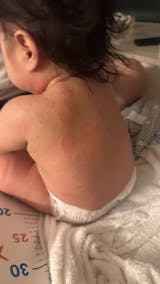
Folliculitis is a skin condition caused by inflammation of the hair follicles, typically appearing as red bumps or small pus-filled spots that may be painful or itchy. The most common cause is bacterial infection, particularly Staphylococcus aureus, though other triggers include fungal infections, shaving irritation, friction from clothing, or weakened immunity. It often occurs in areas such as the beard, scalp, back, and thighs.
Mild cases of folliculitis can be improved by keeping the skin clean and using natural remedies. However, if symptoms are severe or recurring, it's best to consult a doctor. For daily prevention, ensure shaving tools are clean, wear loose-fitting clothing, and keep the skin dry to avoid excessive friction or heat buildup.

Folliculitis Symptoms: How to Tell If You Have Inflamed Hair Follicles
Early symptoms of folliculitis are often mistaken for acne, but the two differ slightly in appearance and texture. Folliculitis refers to inflammation of the hair follicles and is typically accompanied by the following common symptoms:
Red, Swollen Bumps
The affected area develops small red bumps, usually centered around hair follicles. They may feel slightly firm to the touch and are often accompanied by local swelling or warmth.
Pus-Filled Spots or Pimples
As folliculitis worsens, small pustules may form on the skin's surface, resembling pimples filled with white or yellow pus. These may drain when pressed.
Itching or Stinging Sensation
Many people experience mild to moderate itchiness, sometimes accompanied by a stinging or burning feeling. These symptoms can worsen with scratching or friction.
Recurring Breakouts, Scabbing, or Dark Marks
Chronic folliculitis may reappear in the same areas, and after healing, it can leave behind scabs or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, affecting the skin’s appearance and texture.
Common Areas Where Folliculitis Occurs
Face (especially the beard area in men)
Folliculitis often appears after shaving, especially if razors are unclean or technique is rough. Tiny skin cuts can let bacteria in, leading to inflammation. Greasy post-shave products may clog pores, and fast beard growth or oily skin can make men more prone to it.
Scalp
The scalp produces a lot of oil, which can clog follicles. Product buildup from shampoos or hair styling can also irritate the skin. Wearing hats or helmets traps heat and moisture, encouraging bacterial growth. Scratching the scalp with nails can worsen the condition.
Back
Common in people who sweat a lot, especially after exercise. Sweat mixed with oil and friction from clothing can inflame follicles. Wearing damp clothes too long or not cleaning the back properly adds to the risk. Dead skin buildup is another trigger.
Inner Thighs
Tight pants, sitting for long periods, or thigh friction from walking can lead to folliculitis. Humidity and sweat buildup in this area make things worse. It’s also common in people who are overweight or wear non-breathable fabrics like tights or leggings.
Buttocks
Prolonged sitting reduces airflow and increases pressure on the skin. If underwear isn’t breathable, the area stays warm and moist, allowing bacteria to grow. Since hair follicles here are deeper, inflammation can be more painful and persistent.
What Are The Causes Of Folliculitis?
Bacterial Infection (e.g. Staphylococcus aureus)
The most common cause of folliculitis is infection by Staphylococcus aureus, a type of bacteria commonly found on the skin and in the nasal passages. When the skin has small cuts, is scratched excessively, or if hygiene is poor, the bacteria can enter and inflame the hair follicles. The risk increases in humid climates or when sweating is excessive.
External Irritation: Shaving, Friction, Heat and Humidity
Frequent shaving or wearing non-breathable clothing can irritate hair follicles and trigger inflammation. When the skin is exposed to heat, moisture and friction for extended periods such as wearing tight pants or not cleansing the skin promptly after exercise, pores can become clogged, creating an ideal environment for bacteria to grow.
These situations are especially common during summer or among people who exercise regularly. Wearing breathable, sweat-wicking clothing and washing up after sweating is recommended.
Low Immunity and Sensitive Skin
When the immune system is weakened due to chronic stress, lack of sleep, or underlying health conditions, the skin’s natural defenses are compromised, making it more vulnerable to bacterial or fungal infections. People with sensitive skin also have a weaker skin barrier, making them more prone to folliculitis, redness, and itchiness.
How to Treat Folliculitis?
Treatment for folliculitis depends on the severity of the condition. Mild cases can often be managed by keeping the affected area clean, using antibacterial products, and applying topical antibiotic creams. For moderate to severe infections, medical attention is recommended. Treatment may involve oral antibiotics, antifungal medications, or drainage of the infected area if necessary.
For daily care, it's important to wear breathable clothing, cleanse sweat promptly, avoid oily skincare products, and maintain hygiene of shaving tools. These steps are essential for both preventing and managing folliculitis.
Natural Treatments and Recommended Ingredients for Folliculitis
Warm Compress
Benefits: Applying a warm, damp cloth to the affected area can reduce inflammation, soothe irritation, and help drain pus.
How to Use: Soak a clean towel in warm (not hot) water, wring it out, and place it on the affected area for 15–20 minutes. Repeat 3–4 times daily.
Tea Tree Oil
Benefits: Tea tree oil has antibacterial, antifungal, and anti-inflammatory properties that help combat bacterial or fungal folliculitis.
How to Use: Dilute a few drops of tea tree oil with a carrier oil (like coconut or olive oil) at a 1:10 ratio. Apply to the affected area with a cotton swab 1–2 times daily. Always do a patch test first to avoid skin irritation.
Coconut Oil
Benefits: Rich in lauric acid, coconut oil has natural antibacterial effects and also helps moisturise and protect the skin.
How to Use: After cleansing, apply a thin layer of virgin coconut oil to the affected area once or twice a day.
Aloe Vera
Benefits: Aloe vera is known for its soothing, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial effects. It can reduce redness and support skin healing.
How to Use: Apply fresh aloe vera gel (directly from the plant or a pure organic product) to the affected area. Leave it on for 20–30 minutes, then rinse off. Repeat 1–2 times daily.
Apple Cider Vinegar
Benefits: Apple cider vinegar has antibacterial and antifungal properties and helps balance the skin’s pH.
How to Use: Dilute one part apple cider vinegar with three parts water. Apply to the affected area using a cotton ball, leave on for 10–15 minutes, then rinse off. Use once or twice daily. Avoid using on broken or highly irritated skin.
Turmeric
Benefits: Turmeric contains curcumin, a compound with strong anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties.
How to Use: Mix a small amount of turmeric powder with water or honey to form a paste. Apply to the affected area for 15–20 minutes, then rinse off. Use once a day. Note: turmeric may temporarily stain the skin or clothing.
Oatmeal Bath
Benefits: Oatmeal has anti-inflammatory properties that help soothe itching and irritation caused by folliculitis.
How to Use: Add 1–2 cups of finely ground colloidal oatmeal to warm bath water. Soak for 15–20 minutes, then gently pat the skin dry.
Recommended Products for Treating Folliculitis

No No Itchy Gel
An all-natural anti-itch balm helps relieve redness and itching caused by folliculitis. The formula contains aloe vera juice, tea tree oil, calendula, and chamomile oil, which work to reduce inflammation, fight bacteria, soothe the skin, and support the healing of irritated hair follicles. It is suitable for early-stage folliculitis and for daily care during recurring flare-ups.
View Product
Moisturising Zinc Oxide
This 100% natural aloe vera and zinc oxide ointment is a gentle skincare option specifically designed for folliculitis-prone skin. Compared to traditional zinc oxide creams, it offers enhanced hydration and repair. The natural aloe vera soothes redness and itching caused by inflamed hair follicles, while zinc oxide forms a protective barrier on the skin's surface, shielding it from external irritants and moisture. This helps support faster healing of damaged follicles.
View Product5 Daily Habits to Prevent Folliculitis
Keep Skin Clean and Dry
Rinse off sweat promptly, especially on areas like the back and underarms. Use a gentle antibacterial body wash containing ingredients like tea tree oil or chamomile. Avoid over-washing, which can damage the skin barrier.
Practice Proper Hair Removal
Before shaving, soften hair with a warm towel for about 3 minutes. Use a clean, sharp razor and shave in the direction of hair growth to reduce irritation.
Wear Breathable Clothing
Choose loose-fitting cotton clothes to minimise friction and heat buildup. Change out of sweaty clothes quickly after exercising, and avoid wearing tight pants or compression garments for long periods.
Strengthen Your Immune System
Maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins A, C, and zinc. Prioritise good sleep, regular exercise, and stable blood sugar levels, as people with diabetes are more prone to recurring infections.
Practise Good Hygiene in Public Spaces
Disinfect gym equipment before use, and avoid sharing personal items like towels or razors with others. This helps reduce the risk of bacterial transmission.
Summary
Folliculitis is a skin inflammation caused by bacterial or fungal infection of the hair follicles. Common symptoms include redness, pustules, and itching. Key causes include shaving irritation, friction from clothing, and weakened immunity. Mild cases can be treated with topical antibiotics, while more severe cases may require oral medication or drainage. Prevention focuses on keeping the skin clean and dry, wearing breathable clothing, and practising proper hair removal techniques. If symptoms persist or worsen, medical attention is recommended.











Leave a comment