Comprehensive Guide to Urticaria: From Causes to Treatments
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a frequent skin condition that can significantly affect one’s quality of life. This article explores all aspects of the disorder, helping you develop a clear understanding and effective approach to management.
Table of Content
What is Urticaria?
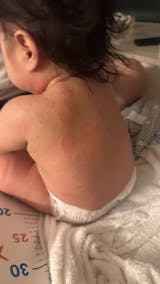
Urticaria, also known as “hives” or “welts,” is an allergic skin reaction characterized by raised, red or skin-colored welts with clearly defined borders, accompanied by intense itching. The duration of symptoms distinguishes acute from chronic urticaria: acute cases resolve within six weeks, while chronic urticaria may recur for over six weeks, lasting months or even years.
Severity varies greatly among individuals. Mild cases involve localized skin irritation, while severe cases may include angioedema, swelling of the lips, eyelids, or other areas - and even life-threatening respiratory difficulty.
Causes of Urticaria
Urticaria can be triggered by a wide range of factors, generally categorized into three groups:
1. Allergen Exposure
Common allergens include:
Foods: seafood, nuts, eggs, and others
Medications: antibiotics, pain relievers
Environmental triggers: pollen, dust mites, pet dander
2. Physical Triggers
Certain physical stimuli can directly cause urticaria:
Pressure-induced: swelling in areas under pressure
Cold-induced: exposure to low temperatures
Heat-induced: triggered by elevated body temperature
Solar-induced: reaction after sun exposure
3. Internal Factors
Emotional stress and mood fluctuations are often hidden causes of chronic urticaria. Autoimmune disorders and thyroid diseases can also provoke flare-ups through complex immune mechanisms. Viral infections, either during illness or recovery, may trigger temporary episodes.
Common Symptoms of Urticaria
The most typical symptom is sudden itching, followed by raised, red welts of varying sizes that can appear and disappear within hours, often reappearing elsewhere. Itching tends to worsen at night, disrupting sleep.
Other symptoms may include:
Burning or stinging sensations
Localized swelling
Fatigue or discomfort
Occasional mild fever
⚠️ Warning: If you experience difficulty breathing, swelling of the lips or tongue, or dizziness, seek immediate medical attention, as these may be signs of anaphylaxis.
|
Symptom |
Appearance |
Trigger |
Consequence |
|
Red rash & welts |
Raised red or pink patches with pale centers |
Allergens (food, medication, pollen, dust mites), insect bites |
Severe itching, can spread across body |
|
Intense itching |
Uncontrollable urge to scratch |
Stress, temperature change, sweating |
Skin damage, infection risk |
|
Localized swelling |
Eyelids, lips, hands, feet swelling |
Allergic reaction, chemical contact |
May cause breathing difficulty (urgent) |
|
Burning/stinging |
Skin feels hot or irritated |
Heat, sun exposure, exercise |
Increased sensitivity, inflammation |
|
Recurrent outbreaks |
Rash appears and fades repeatedly |
Autoimmune issues, chronic allergy |
Chronic urticaria, reduced life quality |
Recommended Skincare Products For Urticaria
No No Itchy Gel
Formulated for sudden redness, itching, and allergic reactions. Contains natural aloe vera, chamomile, and mint extracts to instantly cool and calm the skin, reducing redness and swelling.
Light, non-sticky texture absorbs quickly. Free from steroids and artificial fragrances, making it safe for daily use - ideal for urticaria triggered by climate changes, stress, or insect bites.

Hydro-Moisturiser
Dryness and irritation can worsen urticaria. This restorative cream, enriched with mallow root extract, jojoba oil, and cucumber extract, deeply hydrates and strengthens the skin barrier.
With added vitamin C and shea butter, it locks in moisture, soothes inflammation, and maintains soft, balanced skin. Consistent use helps reduce flare-ups and improve skin resilience.

Rejuvenating Facial Serum
Contains high concentrations of hyaluronic acid, sodium PCA, heptapeptide-8, and tocopherol (vitamin E) to penetrate deep layers of the skin.
Hyaluronic acid repairs dryness and barrier damage caused by urticaria.
Sodium PCA, a natural moisturizing factor, attracts and locks in hydration.
Heptapeptide-8 relaxes facial tension, improving texture and reducing stress-induced inflammation.

Nourishing Body Wash
A gentle cleanser for dry, sensitive, or urticaria-prone skin. Made with natural coconut-based surfactants, it’s free from soap, alcohol, and fragrance.
Infused with calendula and aloe vera, it cleanses while soothing irritation, preventing post-wash tightness and itchiness - turning your shower into a calming skincare ritual.

Natural Remedies for Urticaria
For those seeking mild yet effective natural relief, these home methods can complement medical treatment:
Cooling Compresses
Applying a clean towel soaked in cold water to affected areas for 15–20 minutes several times daily helps constrict blood vessels and relieve redness and itching. For added effect, use refrigerated chamomile tea, which has natural anti-inflammatory properties.
Oatmeal Baths
Colloidal oatmeal forms a soothing protective layer on the skin, locking in moisture and calming irritation. Add finely ground oats to cool or lukewarm bathwater and soak for 15–20 minutes. Pat skin dry and apply moisturizer immediately for best results.
Aloe Vera’s Dual Benefits
Fresh aloe vera gel provides cooling relief while delivering polysaccharides and antioxidants that repair the skin barrier. Choose high-purity aloe products and apply 2–3 times daily. Perform a patch test first to ensure no sensitivity.
Conclusion
Effective management of urticaria begins with understanding its triggers and progression patterns. Because the causes are complex and varied, a targeted and staged treatment plan - focusing on identifying triggers and strengthening the skin barrier - is essential for long-term stability and comfort.














Leave a comment